
phellinus igniarius medicinal Products, it is mulberry branches and fungi grow out, similar to mushrooms.
Major markets, USA, Western Europe, Southeast Asia, Japan and Korea. We can provide Phellinus linteus products and free samples for your testing.
Why is phellinus igniarius medicinal?
The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Phellinus igniarius mushroom extract in multiple sclerosis animal models. Medicinal mushroom Phellinus igniarius contains bioactive compounds that regulate human immune system. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) was induced by immunization with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG 35-55) in C57BL/6 female mice. During the whole experiment, Phellinus igniarius (Piwep) water-ethanol extracts were delivered to the peritoneum every other day. Demyelination and infiltration of immune cells in the spinal cord were examined 3 weeks after initial immunization.
Piwep injection significantly reduced the daily morbidity and clinical score of EAE. Piwep-mediated inhibition of EAE clinical processes is accompanied by inhibition of demyelination and infiltration of CD4 + T cells, CD8 + T cells, macrophages and B-cell-induced inflammatory immune cells in the spinal cord. Piwep decreased the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in spinal cord and integrin in lymph nodes of EAE mice. Piwep also inhibited lymphocyte proliferation and interferon secretion in lymph nodes of EAE mice. The results showed that mushroom extract Piwep may have a high therapeutic potential to improve the progression of multiple sclerosis.
Phellinus igniarius treating inflammation and cancer
Mushrooms belonging to the genus Hymenochaetaceae Basidiomycetes have traditionally been used as Asian drugs to treat inflammation and cancer, and their medicinal functions are being studied. The most prominent discovery of mushroom’s medicinal function is that polysaccharides extracted from Phellinus igniarius have strong immunomodulatory properties and can be used to treat inflammation and cancer. Phellinus igniarius is another kind of mushroom belonging to Phellinus. It is also used as a herbal medicine in Asia.
Mouse immune cell research
Its immunomodulatory properties have been reported. Polysaccharides, especially dextran, are believed to be responsible for the observed biological activity in these medicinal mushrooms. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to determine the potential therapeutic effect of the extract of Phellinus igniarius on multiple sclerosis.
One of the most commonly used animal models of multiple sclerosis is experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), which is induced by immunization with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). Using an EAE mouse model induced by MOG, we studied whether systemic delivery of mushroom extract (Piwep) could inhibit clinical progression and pathological changes. In this study, Piwep improved the severity of EAE in MOG-injected mice, along with the decrease of demyelination, the decrease of microglia activation and the inhibition of inflammatory immune cells in invasive encephalitis. These results suggest that the mushroom extract Piwep has potential therapeutic effects on MS.
Can the contribution of phellinus igniarius to gastric cancer be cured?
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fourth most common cancer in the world and the second leading cause of cancer death. Phellinus igniarius is a traditional medicinal mushroom used in China and other East Asian countries to treat various diseases, including cancer. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antitumor activity of P. igniarius and elucidate its possible mechanism. MTT experiments show that P. The total ethanol extract of igniarius (TPI) has anti-tumor activity against five human cancer cell lines: HepG-2, AGS, SGC-7901, Hela and A-549. TPI was found to have the strongest cytotoxicity to gastric cancer SGC-7901 in vitro and strongly inhibit the growth of xenografted nude mice. Typical morphological changes induced by apoptosis were observed in SGC-7901 cells after TPI treatment, including chromatin concentration, nuclear fragmentation and formation of apoptotic bodies.
How is the cytotoxicity of gastric cancer SGC-7901?
TPI blocked the cell cycle of SGC-7901 at G0/G1 phase and induced apoptosis by down-regulating the expression of cyclin D1. TPI induced a significant decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP, m) in SGC-7901 cells, and induced mitochondrial-dependent cell apoptosis by triggering caspase-9, -3 activation and PARP lysis. In addition, TPI increased the proportion of Bax/Bcl-2 in SGC-7901 both in vitro and in vivo. These results show that P. Igniarius may be a potential natural derivative therapy for the prevention and treatment of gastric cancer, because it can induce cancer cell apoptosis through mitochondrial dependent pathway.
How to extract Phellinus igniarius ingredients?
Basidiomycetous mushroom Phellinus igniarius (L.) Quel. For many years, it has been used as traditional medicine in Asian countries. Although there are many reports about its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and therapeutic effects on various diseases, our current knowledge of its effects on stroke is very limited. It was found that the polyphenol extract from Phellinus igniarius has strong antioxidant activity. The dried results of wild mulberry and mulberry powder are provided by Amazing Grace Health Products Limited Partnership (Bangkok, Thailand). They were extracted with 70% ethanol (10% w / v) at 70 ~C for 16 hours. The supernatant was removed by centrifugation of 10,000 g for 20 minutes. The ethanol extracts of crude Phellinus igniarius (PL EtOH) and Phellinus igniarius (PIEtOH) were filtered and stored at – 20 C for further use. Crude water extract was prepared by hot water extraction [30] for 16 hours. Then the water extracts of Phellinus igniarius (PL DDW) and Phellinus igniarius (PIDDW) were filtered and stored at – 20 C for further use. The ethanol extracts of Phellinus igniarius (PI EtOH) and Phellinus igniarius (PLEtOH) were lyophilized and stored at – 20 C for further use.
Laboratory Phellinus igniarius molecular picture
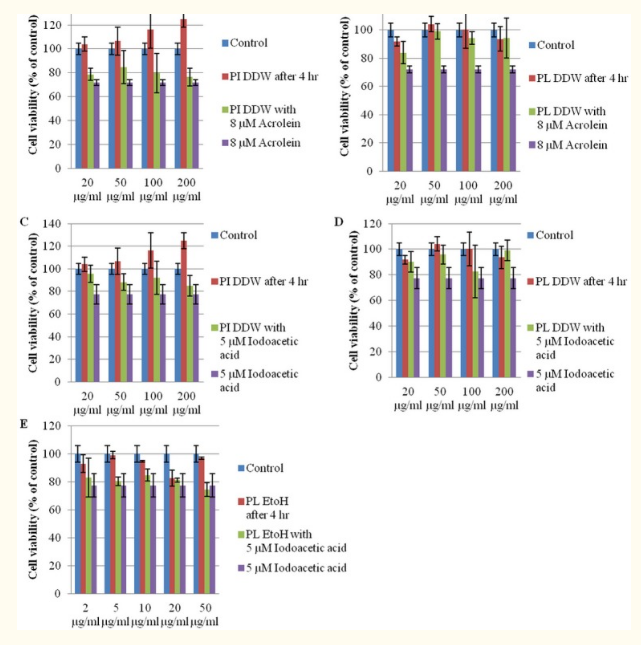
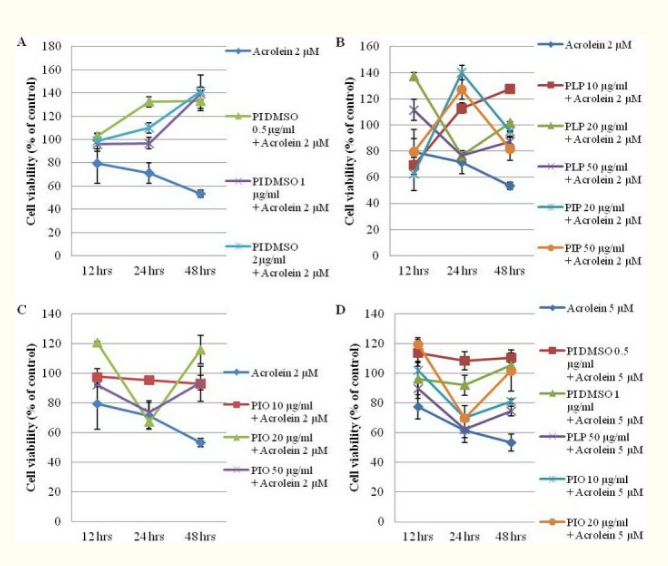
Image Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4374876/
Phellinus igniarius Antibacterial, anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, anti-diabetic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects
Phellinus igniarius is a species reported to have antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-diabetic and anti-hyperlipidemia properties. The aim of this study was to elucidate the changes of endogenous metabolites after oral administration of Ph. Igniarius decoction. The results showed that Ph. Igniarius could increase the biosynthesis and secretion of bile acid and provide hypolipidemic activity. It also indicated that UPLC/ESI-HDMS technology was promising for the analysis of metabolites in medicinal mushrooms. Medicinal mushrooms occurring in southern India, namely Ganoderma lucidum, mulberry yellow, Pleurotus Florida and Pleurotus pulmonaris, have profound antioxidant and antineoplastic activities.
World class baby
This indicates that these mushrooms are valuable sources of antioxidants and antineoplastic compounds. The investigation also showed that they had significant antimutagenic and anticancer activities. Therefore, Indian medicinal mushrooms are potential sources of antioxidants and anticancer compounds. Edible and medicinal fungi (mushrooms) are widely used in functional foods and nutritional health products because of their proven nutritional and medicinal properties. Phellinus sensu lato is a famous medicinal mushroom, which has long been used to prevent diseases in eastern countries, especially in China, Japan and Korea, including gastrointestinal dysfunction, diarrhea, bleeding and cancer. Polysaccharide is one of the main bioactive molecules in Phellinus igniarius. L. It has remarkable antineoplastic, immunomodulatory and medicinal properties.
Mulberry Huang’s contribution to current medicine
To study the inhibitory effect of the extract of medicinal fungus Phellinus igniarius on S180 tumors and the immunomodulatory effect on S180-induced tumors in mice. S180 mice were orally administered with 100,200,400 mg *kg(-1) of P. igniarius extract, and then the growth inhibition effect, spleen index and thyme index were measured. The extracts of P. igniarius could increase spleen index and thyme index, and the inhibition rates were 31.88%, 46.25% and 53.13%, respectively. In addition, the extract of P. igniarius can prolong the life of mice. The extract of P. igniarius has obvious antineoplastic and immunomodulatory effects.
The most prominent discovery of the medicinal function of mushrooms is that polysaccharides extracted from Phellinus igniarius have strong immunomodulatory properties and can be used to treat inflammation and cancer.
Can Phellinus igniarius regulate the body’s immune system?
Medicinal mushroom Phellinus igniarius contains bioactive compounds that regulate human immune system. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) was induced by immunization with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG 35-55) in C57BL/6 female mice. During the whole experiment, Phellinus igniarius (Piwep) water-ethanol extracts were delivered to the peritoneum every other day.
To evaluate the therapeutic potential of Phellinus igniarius mushroom extract in multiple sclerosis animal models. Medicinal mushrooms (Phellinus igniarius) contain bioactive compounds that regulate the human immune system. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is induced by immunization of mice with myelin-sheathed cerebellar meningoprotein. Strains belonging to the basidiomycetes of Polygonaceae have traditionally been used as Asian drugs for cancer and cancer, and their medicinal functions are being studied.
Other mushroom medicinal introduction
The scientific evidence for this mushroom is strong. If you have any type of cancer, you need to take Coriolus versicolor (Turkish tail mushroom). (It’s also known as Trametes versicolor, but in most research and manufacturing it’s called Coriolus versicolor.) In this update, there are too many studies on this medicinal mushroom to completely cover it, so I will focus on some of the most recent, and most notable. Another of my favorite medicinal mushrooms is Lion’s Mane.
Treatment uses include Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, post-stroke dementia, anxiety and depression. Recent research reviews many articles on how different medicinal mushrooms play a role in brain health, pointing out that “mushrooms (extracted from basidiocarps/mycelia) or isolated compounds) reduce neurotoxicity induced by beta-amyloid protein, and have anti-acetylcholinesterase, outward growth stimulation of neurites, synthesis of nerve growth factor (NGF), neuroprotection, antioxidant activity.” Anti-inflammation
How Phellinus igniarius was found to be used?
However, some may speculate that tobacco would be a good choice to play a role in celebrations if the King of India was present. If tobacco exists, it can also be said that mushrooms also exist. This mushroom may be a clam called Phellinus igniarius. Phellinus igniarius is classified as a porous bacterium with a porous bottom and basidiomycetes. It is closely related to Phellinus tremulae, which is another cause of tree heart disease.
Phellinus igniarius is also a member of Hymenochaetaceae. Hymenochaetaceae is a highly variable Basidiomycota, which has some microscopic characteristics that combine them. In northern North America, before tobacco arrived, ash from Phellinus igniarius conks was widely used in native plants. Denaina, an Asabaska Indian from the interior of Alaska, chewed a mixture of P. igniarius ash and balsam bark during pre-exposure. Collections from Canadian and American museums show that P. igniarius is used in New Siberia’s Mimac, Labrador’s Inuit, North American Plains’black feet and Kwakiutl’s tobacco in the Pacific Northwest.
